In this section, the physical and logical structure of the device is defined.
The physical structure represents which parts of the device are mechanically connected to each other. The logical structure represents logical dependencies between parts of the device that are needed to describe functions of the device.
A valid GDTF file must have at least one geometry. A geometry can contain a link to a 3D model.
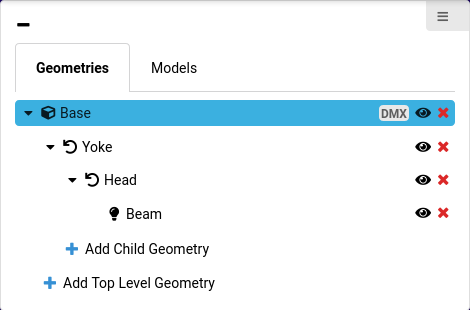
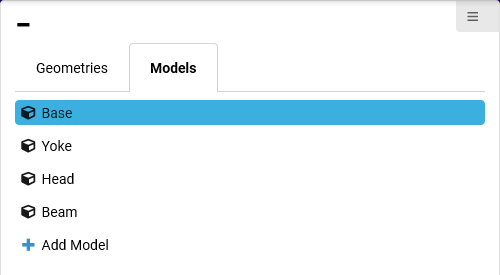
The left part of the Geometry Page shows the Geometries/Models section. In the Geometries section, all geometries are listed in the form of a tree structure. The Models section contains a list of all models that are currently part of the GDTF file.
Clicking on the - icon collapses this section and provides more space for the Properties section.
The Properties section is located below the Geometry Tree section. All properties of the currently selected geometry or model can be viewed and edited here.
Information about the vertices count of the selected geometry and of all geometries can be found at the bottom of the Properties section.
The right part of the Geometry Page shows a 3D view of the device.
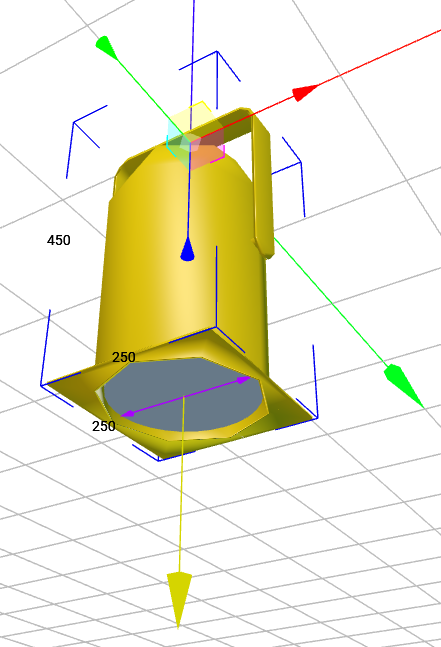
Selected geometries can be moved and rotated using the colored handles.
A blue bounding box is displayed for the currently selected geometry and all of its children. The numbers on the edges indicate the current dimensions (in mm) of the selection.
Yellow arrows are drawn for each Beam geometry. The direction of the arrow indicates the direction of the Beam. Purple arrows on a Beam geometry indicate the Beam Diameter.
The 3D View Settings are located in the top-left corner of the 3D View.